WHAT IS GROUND SOURCE HEAT PUMP?
WHAT IS GROUND SOURCE HEAT PUMP?
1. Definition
Ground-source heat pump system (Ground-source Heat Pump System) refers to a heating and air-conditioning system composed of a water-source heat pump unit, a geothermal energy exchange system, and a building system that uses rock and soil, groundwater, or surface water as a low-temperature heat source.
Let's first understand the "heat pump". Heat pump (refrigerator): It is a device that causes heat to flow from a medium with a low temperature to a medium with a high temperature through work. The low-temperature heat source utilized by the heat pump is usually the environment (atmosphere, surface water, and the earth) or various waste heat, and the heat absorbed by the heat pump from these heat sources is a renewable energy source. Heat pumps are a sustainable technology that utilizes renewable energy and protects the environment. A heat pump that uses the earth (soil, stratum, underground water) as a heat source can be called a ground source heat pump.
2. Characteristics
1. Energy saving and high efficiency
Under the condition of the same power consumption, the cooling capacity in summer and the heat supply in winter are respectively increased, and the energy efficiency ratio EER: 3.9-6, that is, 3.9-6KW heat energy can be obtained by inputting 1KW electric energy in summer, and the coefficient of performance COP=2.65-5. In winter, when 1KW of electric energy is invested, about 3.0-5KW of heat energy can be obtained; and the underground pipe heat exchanger does not require defrosting, which reduces the energy consumption of frosting and defrosting.
2. Stable performance
Stable underground temperature: The average underground temperature is basically stable between 16°C and 22°C. It is not affected by the temperature change of the outdoor ambient air. The cooling and heat of the main engine are stable, and there will be no air source heat pump. The more it needs air conditioning, the worse it will be .
3. High return on investment
As a building air conditioning system, the ground source heat pump system can greatly reduce its operating costs. When the ground source heat pump system is used for heating or cooling, according to different regions, climates, resources, and environments, the operating cost can be reduced by 25%-50% compared with traditional central air-conditioning systems; Domestic hot water can be combined into one of cold, warm and hot water; one system can replace the original two sets of devices or systems of boiler and air conditioner, reducing the initial investment of equipment; the payback period of the initial investment increment of the ground source heat pump system is about 2.5-8 years wait.
4. Renewable energy utilization technology
Surface soil and water bodies collect 47% of solar radiation energy, which is more than 500 times the energy used by humans every year. The soil and water bodies on the surface naturally maintain a relative balance in energy reception and emission. The secondary utilization of solar energy is in line with the trend of sustainable development and is not restricted by geography, resources, etc.
5. Environmental protection
Pollutant emissions are reduced by more than 40% compared to air source heat pumps and 70% compared to electric heating. There is no combustion, smoke exhaust, or waste, and there is no need to transport heat over long distances. It is a truly environmentally friendly air conditioner. In summer, heat will not be released to the air around the building to increase the ambient air temperature, and in winter, heat will not be absorbed from the air around the building to lower the ambient air temperature. The unit's underground heat exchanger can be placed underground in gardens, lawns and around buildings without occupying building area.
6. Safety and long life
The ground source heat pump is very durable, and there are very few mechanical moving parts (the host is assembled as a whole by the factory). All the parts are buried underground or installed indoors, thus avoiding the harsh outdoor weather. The system adopts a closed cycle to reduce corrosion, pollution and knots. The maintenance cost of the system is low; the underground part (PE pipe) can be guaranteed for 50 years (maintenance-free), and the maintenance is mainly for the water pump, indoor pipeline and indoor unit --- simple maintenance, small workload, saving Maintenance costs; the normal life of a ground source heat pump unit is 25 years.
7. Wide range of applications
Wide application: It can be applied to new construction, reconstruction and expansion projects that require air conditioning in hotels, shopping malls, office buildings, schools and other buildings, and is more suitable for heating and air conditioning in villas;
shortcoming
① If used unreasonably, it may cause serious pollution to groundwater.
② If groundwater is extracted in large quantities and cannot be recharged in time, it may cause ground subsidence and damage to buildings on the ground.
③Not suitable for: places with high building density and areas with harsh geological conditions (such as underground rock formations that are thick and hard)
3. Application and Development
The concept of ground source heat pump first appeared in a Swiss patent document in 1912.
Open groundwater heat pump systems were successfully used in the 1930s.
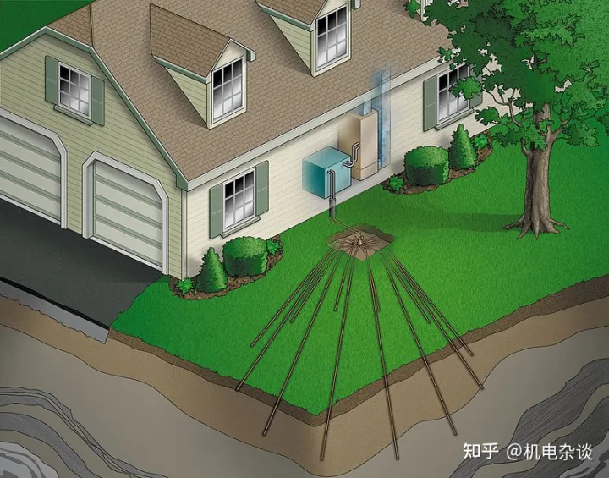
In the 1950s, Europe and the United States set off the first climax of research on ground source heat pumps. The Edison Institute of Electronics in the United States was the first to study closed-loop heat pump systems, and Indianapolis in Indiana was the first to install closed-loop heat pumps. Loop ground source heat pump system.
Until the 1970s, the world oil crisis made people pay attention to energy conservation and high energy efficiency, and the research on ground source heat pumps entered another climax. At this time, Swedish researchers began to apply plastic pipes to closed loop ground source heat pump systems. The popularization and application of ground source heat pumps has been carried out rapidly.
After nearly 50 years of development, ground source heat pump technology has become very mature in North America and Europe and is a widely used heat pump air conditioning system. There is a complete set of standards, specifications, calculation methods and construction techniques for system design and installation of ground source heat pump units and geothermal heat exchangers.
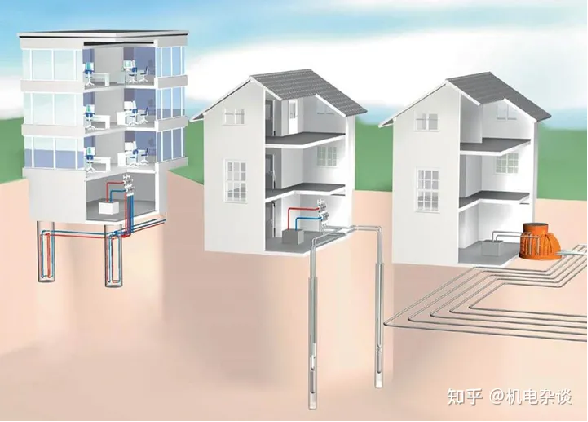
By the end of 2019, more than 30,000 systems were used in homes, schools, and commercial buildings in the United States. According to statistics from the Ground Source Heat Pump Association, more than 600 schools in the United States have installed geothermal heat pump technology.
04. Working principle
As a natural phenomenon, just as water flows from a high place to a low place, heat always flows from a high temperature to a low temperature, which is accurately expressed by the famous second law of thermodynamics: "Heat cannot be spontaneously transferred from a low temperature to a high temperature". But people can create machines that can pump heat from low to high temperatures, just as water pumps are used to lift water from low to high. Therefore, the ground source heat pump is essentially a heat raising device. It consumes part of the energy itself, excavates the energy stored in the environmental medium, and raises the temperature level for utilization. The work consumed by the entire heat pump device is only three times the heat supply. One percent or less, this is the principle of energy saving of ground source heat pump.
In winter, the heat pump unit absorbs heat from the ground source (shallow water or rock and soil) to heat the building;
In summer, the heat pump unit absorbs heat from indoors and transfers it to the ground source to realize air conditioning and cooling of the building.
Working principle of ground source heat pump in winter
In winter, the refrigerant in the heat pump flows in the forward direction, and the high-temperature and high-pressure gas discharged from the compressor enters the condenser to release heat to the water in the water collector, and the phase changes into a high-temperature and high-pressure liquid, which is then throttled and reduced by the thermal expansion valve to become a low-temperature and low-pressure gas. The liquid enters the evaporator, absorbs low-temperature heat from the underground circulating liquid, and then transforms into low-temperature and low-pressure saturated steam, then enters the suction end of the compressor, and is compressed by the compressor to discharge high-temperature and high-pressure gas to complete a cycle. In this cycle, the underground low-temperature heat energy is "transported" to the water collector, thereby continuously providing hot water of 45°C-50°C to users.
Working principle of ground source heat pump in summer
In summer, the refrigerant in the heat pump flows in reverse, and the condenser that exchanges heat with the user becomes an evaporator to extract heat energy from the low-temperature water (7°C-12°C) in the water collector, and the evaporator that exchanges heat with the underground circulating fluid becomes a condenser The heat is discharged to the underground circulating fluid, and the heat in the circulating fluid is discharged to the underground low-temperature area, so as to continuously provide users with cold water at 7°C-12°C.
5. Classification
According to the different forms of geothermal energy exchange systems, ground source heat pump systems are divided into buried pipe ground source heat pump systems, groundwater ground source heat pump systems and surface water ground source heat pump systems.
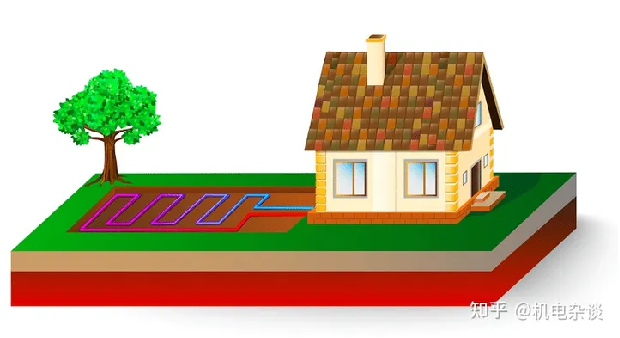
1. Buried pipe ground source heat pump system
The underground pipe ground source heat pump system is a ground source heat pump system that utilizes closed-circuit circulation of heat in underground rock and soil. It realizes heat transfer between the system and the earth through the flow of circulating fluid (water or antifreeze containing water as the main component) in closed underground buried pipes.
Vertical Configuration of Ground-Coupled Heat Pump Systems
Horizontal Configuration of Ground-Coupled Heat Pump Systems
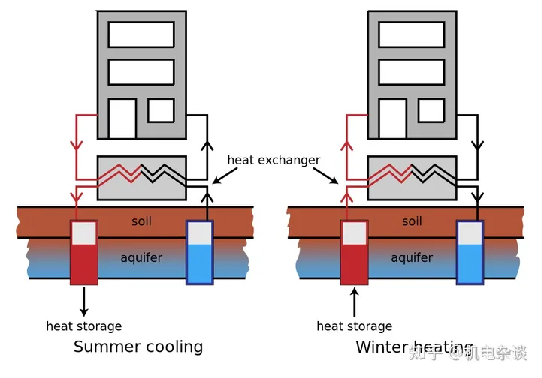
2. Groundwater ground source heat pump system
The heat source of the ground water ground source heat pump system is ground water pumped from wells or abandoned mines. The heat-exchanged groundwater can be discharged into the surface water system, but for larger applications it is usually required to recharge the groundwater to the original groundwater layer through the recharge well. The groundwater with good water quality can directly enter the heat pump for heat exchange, and then refill the well water underground. Such a system is called an open system.
Groundwater heat pump system
3. Surface water ground source heat pump system
The heat source for surface water heat pump systems is surface water in ponds, lakes or streams. It is worth considering a type of air conditioning heat pump to use these natural water bodies as the low-temperature heat source of the heat pump in places close to a large number of natural water bodies such as rivers, lakes and seas.
Surface water heat pump system
